Airbus is one of the world’s leading aerospace manufacturers, creating innovative products and solutions that push the boundaries of what is possible. As part of this mission, Airbus, along with five other companies, has developed a new generation of collaborative robots known as Airbus Air COBOT.
The Air COBOT stands for Aircraft Inspection enhanced by smaRt and Collaborative rOBOT. This advanced robot system is designed to work seamlessly with human operators, helping to improve safety, efficiency, and productivity in aerospace manufacturing and assembly.
Airbus has already filed a patent for state-of-the-art collaborative technology on 23 October 2014. To explain the system, Airbus Group distributed a project presentation video made by the communication agency Clipatize on its YouTube channel.

Air Cobot Overview
Airbus Air COBOT is a modular collaborative robot system that is precisely designed to work alongside human operators in aerospace manufacturing and assembly domains.
The system is comprised of a series of robotic modules that can be configured in a variety of forms to suit distinct manufacturing techniques and assignments. Each module is equipped with state-of-the-art sensors and safety segments that allow it to work safely and efficiently alongside human operators.
One of the key features of the Air COBOT system is its modularity. The system is designed to be easily reconfigured and adapted to suit different manufacturing processes and tasks.
This allows manufacturers to quickly and easily optimize their production lines to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity. Another key feature of the project is its advanced sensing and safety features.
The system is equipped with a variety of sensors that allow it to detect and respond to changes in its environment. This includes sensors that can detect the presence of human operators, as well as sensors that can detect obstacles and other potential hazards.
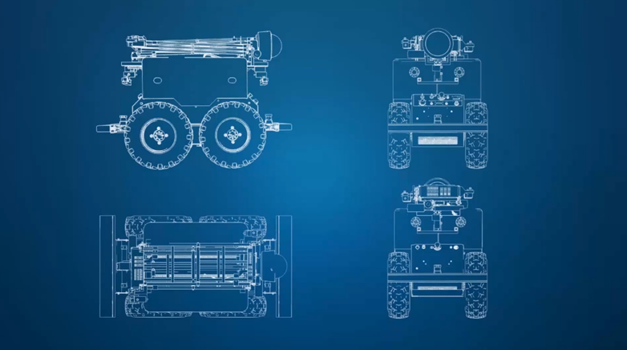
Project Background
The Air-COBOT project was launched in 2013 as a part of the Interministerial Fund program of Aerospace Valley, a business group in southwestern France. A budget of one million euros was allocated to fund the research and development of cutting-edge collaborative robots.
The project was led by Akka Technologies and was divided into two categories. They are academic and industrial and are as follows,
Academic Partners
1) Armines and Institut Clément Ader of the École des mines d’Albi-Carmaux assigned the task to work on Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) technology.
2) Laboratoire d’analyse et d’architecture des systèmes (LAAS-CNRS) with the Robotics, Action and Perception (RAP) team were assigned to work on autonomous navigation systems.
Industrial Partners
1) Akka Technologies Tolouse’s research and development wing is responsible for leading the project and will bring its expertise in image analysis, navigation, and aircraft maintenance.
2) Airbus innovations is the one who initiated the project; it provided the CAD models of its best-seller Airbus A320 and its operational procedures.
3) Another french based company, 2MoRO Solutions, is liable for the maintenance information system-related work.
4) M3 Sytems, a specialist in reliable and accurate geolocation, is accountable for the development of the outdoor localization solution based on GPS.
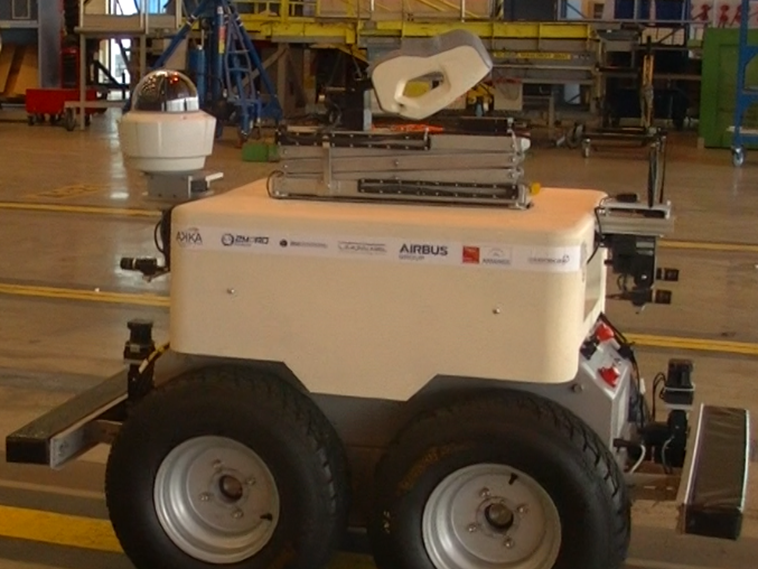
5) At last, Sterela, a smart electronic tech company, is responsible for providing the 4MOB mobile platform.
The task aims to enhance inspections of planes and traceability. They have planned to develop a wide database containing information about aircraft type, its images, 3-D models, and maintenance-related information.

Superior Benefits of Airbus Air Cobot
The Air COBOT offers a range of benefits to aerospace manufacturers and operators. One of the most substantial benefits is improved safety. By functioning alongside human operators, the system can help to lower the risk of accidents and injuries in manufacturing circumstances.
The system’s advanced sensing and safety features also allow it to respond quickly to conceivable threats, further reducing the risk of accidents and injuries.
Another essential advantage of the system is improved efficiency and productivity. By working alongside human operators, the system can help to speed up manufacturing processes and tasks, reducing the time and effort required to complete them.
The system’s modularity also allows manufacturers to quickly and easily optimize their production lines to achieve maximum efficiency and productivity.
It is also prepared to be easy to use and integrate into existing manufacturing territories. The system’s intuitive interface and modular composition make it easy for operators to configure and use. While its compatibility with a variety of other manufacturing procedures and tools makes it easy to integrate into existing manufacturing workflows.
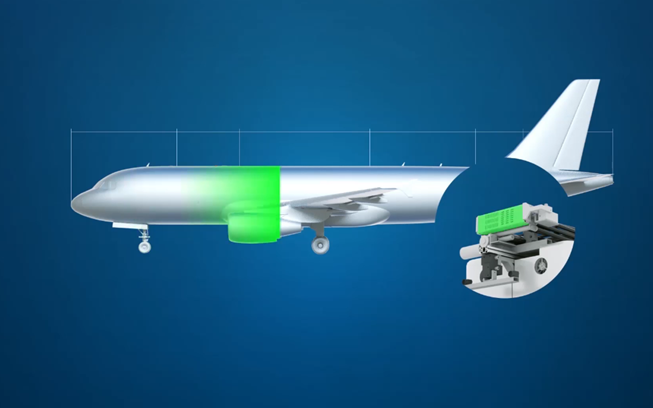
Real-World Applications
The Airbus Air COBOT system has a wide scope of potential applications in the aerospace manufacturing and assembly industry. Some of the most optimistic applications include:
Assembly and Manufacturing: It is ideal for use in assembly and manufacturing circumstances. The system’s modular design and advanced sensing and safety features make it well-suited to a wide range of manufacturing processes and tasks.
Maintenance and Inspection: The system can also be used for maintenance and inspection tasks in aerospace manufacturing and aircraft walk-around inspections. The system’s advanced sensing and safety features make it well-suited to tasks that require proximity to aircraft or other equipment.
Quality Control: The Air COBOT can also be used for quality control tasks in various aerospace domains. The system’s advanced sensing and measurement capabilities make it well-suited to tasks that require precise measurements and data collection.
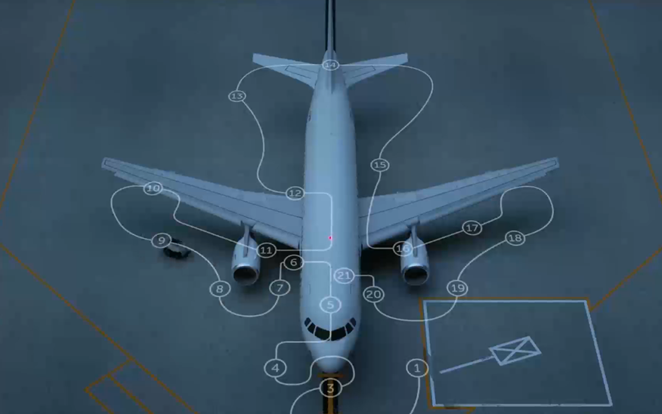

Pre-flight inspections
The company, with the help of the Airbus innovations team, has tested the Air COBOT on the Airbus A320 pre-flight inspection and has summarised it through an animated video created by Clipatize.
There are millions of daily flights, which means there are thousands of aircraft inspection that takes place every hour. However, according to the team working on this project, 70 percent of aircraft inspections are visual inspections, which results in increased downtime and maintenance costs.
The automated robot can help co-pilot and maintenance personnel to perform their duty faster and more efficiently and can do this repeatedly without fatigue. During the pre-flight inspection, it performs a thorough diagnosis in any weather or light conditions, whether it’s snowing, raining, or dark.
The system has a live feed that a pilot or copilot can observe while sitting inside the cockpit; also, they can decide the relevance of diagnosis and approve them accordingly.
With the help of state-of-the-art optical sensors, it can detect scratches, dents, and other damages on the fuselage with high accuracy. It also has anti-collision sensors, which make it safe around aircraft, staff, and compact surroundings.

Future of Manufacturing
This system represents the future of aerospace manufacturing and assembly. With its advanced sensing and safety features, modular design, and compatibility with existing manufacturing systems and tools, the system has the potential to revolutionize the way aerospace products are designed, manufactured, and assembled.
As the aerospace industry continues to evolve, manufacturers and operators will need to embrace new technologies and approaches in order to remain competitive. The Airbus Air COBOT system is one such technology that is poised to transform the industry.
By enabling more efficient and safer manufacturing processes, the system can help aerospace manufacturers to reduce costs, improve quality, and accelerate innovation.
Moreover, the system represents a major breakthrough in the field of collaborative robotics. By working alongside human operators, the system has the potential to transform the way aerospace products are manufactured, assembled, and maintained.
In addition to the benefits of increased safety and efficiency, the use of collaborative robots can also help to manage labor shortages in the aerospace industry. With an aging workforce and a deficiency of skilled workers in many areas, the use of robots can help to fill the gap and ensure that production lines continue to run smoothly.
With a modular design, it can be quickly and easily reconfigured to accommodate transitions in manufacturing processes and tasks. This makes the system ideal for use in fast-paced and dynamic manufacturing environments, where the ability to adapt quickly is essential.

Challenges faced by Airbus Air Cobot
As with any new technology, there are also some potential challenges and concerns associated with the use of collaborative robots in the aerospace industry. One of the main concerns is the potential for job displacement, as robots take over tasks that human workers previously performed.
However, many experts believe that the use of robots will actually create new job opportunities, particularly in areas such as robot programming and maintenance.
Another concern is the potential for cybersecurity risks as collaborative robots become increasingly connected to other manufacturing systems and networks. To address these concerns, it will be important for manufacturers to invest in robust cybersecurity measures and ensure that all connected systems are secure and protected.
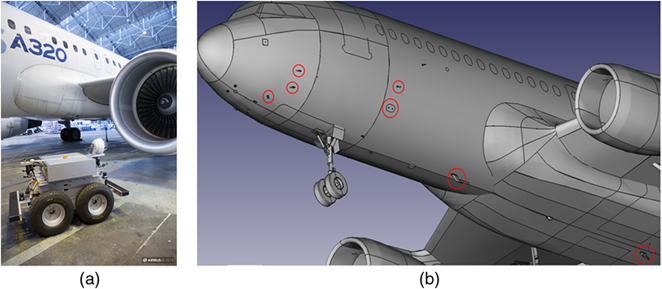
Photo: uploaded by Stanislas Larnier at Research Gate.
Showcase
The automated Air COBOT made its public appearance between 2014 to 2016. During such years, it had five exhibitions which include an appearance in the Paris Air Show of 2015 and the Singapore Air Show of 2016.
Apart from this, the deep research documents about the project were distributed across 18 conferences. During the fifth international conference Machine Control and Guidance (MCG) of 2016, the prize for the best final application is granted to the authors of the publication Human-robot collaboration to perform aircraft inspection in the working environment.
On 17 February 2016, Airbus Group broadcasted a YouTube video presentation of its concept of the hangar of the future in which it intends to use Air COBOT.
Bottom Line
The Airbus Air COBOT system represents a major step forward in the field of collaborative robotics. With its advanced sensing and safety features, modular design, and compatibility with existing manufacturing systems and tools, the system has the potential to transform the way aerospace products are designed, manufactured, and assembled.
In 2015, in an interview given to the French weekly magazine Air & Cosmos, Jean-Charles Marcos, CEO of Akka Research, revealed that once created and marketed, the Air COBOT should cost between 100,000 and 200,000 euros.
As the aerospace industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see more and more manufacturers adopting collaborative robots like the Airbus Air COBOT system in their operations. With their ability to improve safety, efficiency, and productivity, these robots are poised to play an increasingly important role in the future of aerospace manufacturing and assembly.
There are other similar technologies developed by other companies, and some to name are the Donecle drone, EasyJet drone, and European project Robair. We will analyze more such projects in our upcoming articles, so stay tuned with Aviation A2Z always.
However, after 2017 its identity sort of diminished from the industry, and today its official website is inaccessible, and there is no recent development or appearance by the project’s head companies. Even Airbus has deleted the videos it uploaded earlier about the technology.
Do you think collaborative robots like Airbus Air COBOT are future tech for the aerospace industry? Be sure to comment on our social media channels.
Also read: Air India Mega Deal With Boeing And Airbus To Create 2 Lakh Jobs In India | Exclusive
Join us on Telegram Group for Latest Aviation Updates. Furthermore, Follow us on Google News.



































